Guía n° 16 de problemas de desigualdades e inecuaciones
Resolver los siguientes ejercicios
- Escribir en lenguaje de conjunto los siguientes intervalos:
1) ]-∞, 3[ = {x/-∞ < x < 3; x ∈ ℜ}.
2) ]-8, 0] =
3) [-5, 0[ =
4) [- 4, ½] =
5) ]-3, 5[ =
6) [-2, 1] =
7) [-2, 3[ =
8) ]-2, 5] =
9) ]-2, 7[ =
10) ]-1, 5] =
11) [0, ∞[ =
12) [¼, 2[ =
13) [¼, 5] =
14) ]½, 5[ =
15) [3, 6[ =
16) ]4, 8[ =
- Representa en la recta real los siguientes intervalos:
1) ]-∞, 2] =
![]()
2) ]-7, 1] =
3) [-3, 2] =
4) [-3, 0] =
5) ]-2, 1] =
6) ]-2, 7/2] =
7) ]-2, 5[ =
8) ]-1, 5[ =
9) [0, 6[ =
10) [¼, 4] =
11) ]1, 6[=
12) [2, 8] =
13) [3, 7] =
14) ]4, 9] =
15) ]5, 7] =
16) [6, 10] =
- Usando la notación de conjunto; escribir los siguientes intervalos que están representados en la recta real:
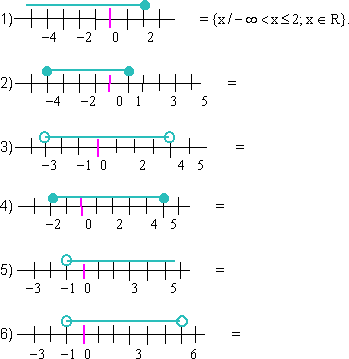
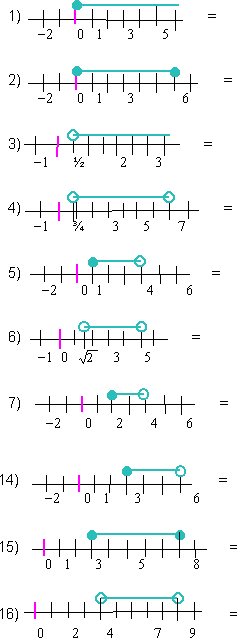
- Usando la notación de intervalos; escribir los siguientes intervalos que están en lenguaje de conjunto:
1) {x/-6 ≤ x < 8; x ∈ ℜ} = [- 6, 8[
2) {x/-4 ≤ x < 0; x ∈ ℜ} =
3) {x/-4 ≤ x < ½; x ∈ ℜ} =
4) {x/-4 ≤ x ≤ 7; x ∈ ℜ} =
5) {x/-3 < x < 1; x ∈ ℜ} =
6) {x/-2 ≤ x ≤ 2; x ∈ ℜ} =
7) {x/-2 ≤ x ≤ 4; x ∈ ℜ} =
8) {x/0 < x ≤ 4; x ∈ ℜ} =
9) {x/0 < x ≤ 5; x ∈ ℜ} =
10) {x/¼ ≤ x < 1; x ∈ ℜ} =
11) {x/⅖ ≤ x ≤ 3/2; x ∈ ℜ} =
12) {x/½ ≤ x < 3; x ∈ ℜ} =
13) {x/⅗ ≤ x ≤ 7/2; x ∈ ℜ} =
14) {x/⅗ ≤ x < 7; x ∈ ℜ} =
15) {x/2 < x < 5; x ∈ ℜ} =
16) {x/3 < x < 7; x ∈ ℜ} =
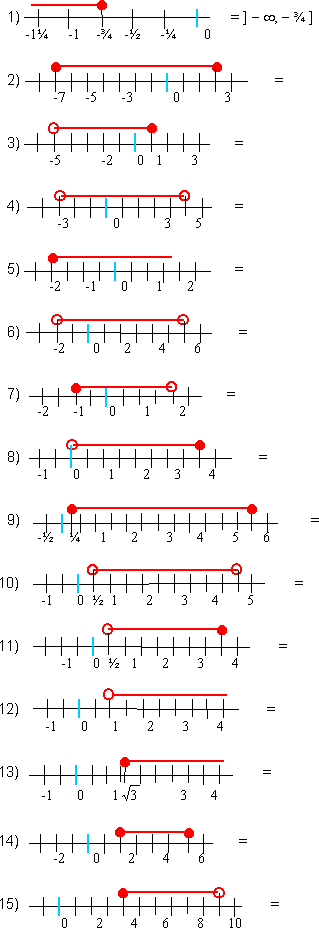
- Usando la notación de intervalos; escribir los siguientes intervalos que están representados en la recta real:
- Resolver las siguientes inecuaciones indicadas:
| Inecuación | Resultado | |
| 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) | 2·x ≥ - 4 14·x ≤ 2·x - 9 x + 1 ≤ 5 x + 2 < 5 2·x + 1 < 9 2·x + 4 > 0 3·x - 2 ≤ 5 3·x - 2 ≤ 13 5·x - 2 ≤ 0 5·x - 3 ≤ 2 1 - x ≤ 5 | x ≥ -2. x ≤ - ¾. x ≤ 4. x < 3. x < 4. x > -2. x ≤ 7/3. x ≤ 5. x ≤ ⅖. x ≤ 1. x ≥ - 4 |
| 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) 21) 22) | 5 - 3·x ≥ -1 3·x - 7 ≤ 3/2 2·x/5 - 1 ≤ 2 x/2 - 3/2 < 0 x/2 - 3 ≤ 5 2·x - 1 ≥ x + 3 3·x + 7 ≥ 2·x - 3 4·x - 5 > 7·x - 3 5·x - 12 > 3·x - 4 2·x - 5/3 > x/3 + 10 3·x - 4 + x/4 < 5·x/2 + 2 | x ≤ 2. x ≤ 17/6. x ≤ 15/2. x < 3. x ≤ 16. x ≥ 4. x ≥ -10. x < - ⅔. x > 4. x > 7. x < 8 |
| 23) | (5 - 2·x)/7 ≤ 3/2 | x ≥ - 11/4 |
| 24) | (11 - 5·x)/2 > (3·x - 5)/4 | x < 27/13 |
| 25) | (2·x + 1)/(3·x - 1) > (2·x + 5)/(3·x + 2) | x < 7/6 |
| 26) | 1/(3·x - 7) ≥ 4/(3 - 2·x) | x ≤ 31/14 |
| 27) | (x + 3)/3 - 4/(x + 2) > x/3 | x > 2 |
| 28) 29) | (x + 2)·(x + 1) + 26 < (x + 4)·(x + 5) (x - 1)² - 7 > (x - 2)² | x > 4/3. x > 5 |
- Resolver las siguientes inecuaciones indicadas con Valor Absoluto
| Inecuación | Resultado | |
| 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) | |x| < 1 |x| > 2 |x| < 3 |x| < 4 |x| ≤ 4 |3·x| ≤ 12 |x/14| ≤ ⅙ |x/4| ≤ 3/2 |2·x/7| ≤ 8 |x - 1| < 3 | -1 < x < 1. -2 > x > 2. -3 < x < 3. - 4 < x < 4. - 4 ≤ x ≤ 4. - 4 ≤ x ≤ 4. - 7/3 ≤ x ≤ 7/3. - 6 ≤ x ≤ 6. -28 ≤ x ≤ 28. -2 < x < 4 |
| 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) | |x + 2| ≤ 5 |x - 2| ≤ 5 |x - 2| ≥ 5 |x - 3| ≤ 3 |x - 4| < 10 |x + 5| < 4 |2·x - 1| < 11 |2·x - 5| < 7 |2·x + 5| < 7 |3·x - 1| ≤ 1 | -7 ≤ x ≤ 3. -3 ≤ x ≤ 7. -3 ≥ x ≥ 7. 0 ≤ x ≤ 6. - 6 < x < 14. - 9 < x < -1. - 5 < x < 6. -1 < x < 6. - 6 < x < 1. 0 ≤ x ≤ ⅔ |
| 21) 22) 23) 24) 25) 26) 27) 28) 29) | |3·x - 9| < 9 |3·x - 9| > 12 |5·x - 4| < 6 |5·x - 4| ≤ 3/2 |8·x - (5·x - 4)| < 6 |8·x - (3·x - 4)| ≤ 6 |2 - x| ≥ 6 |3 - x| < 1 |6 - 4·x| ≤ 8 | 0 < x < 6. -1 > x > 7. - ⅖ < x < 2. ½ ≤ x ≤ 11/10. - 10/3 < x < ⅔. -2 ≤ x ≤ ⅖. 8 ≤ x ≤ - 4. 4 > x > 2. 7/2 ≥ x ≥ - ½ |
| 30) | |x/2 - 2| ≤ 3 | -2 ≤ x ≤ 10 |
| 31) | |x/2 + 5| ≤ ⅔ | - 34/3 ≤ x ≤ - 26/3 |
| 32) | |(5·x + 2)/(x - 2)| < 5/3 | ⅕ < x < - 8/5 |
Autor: Hugo David Giménez Ayala. Paraguay.
Editor: Ricardo Santiago Netto (Administrador de Fisicanet)